Characteristics of X-linked Recessive Disorders Include Which of the Following
Characteristics of X-linked sex-linked recessive disorders include all daughters of affected fathers being carriers. Heterozygous female may have a variable expression of X linked recessive disorder due to the random process of X inactivation involving inactivation of the X chromosome with a mutant allele in some cells while.
Sex-linkage studies in Morgans laboratory provided the fundamentals for understanding X-linked recessive disorders in humans which include red-green color blindness and Types A and B hemophilia.
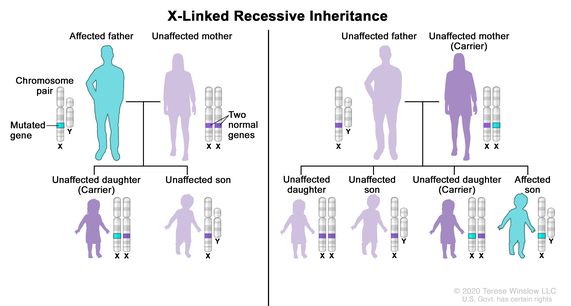
. The Y chromosome is the other half of the XY gene pair in the male. Males are affected by X-linked recessive disorders much more frequently than females. Type A hemophilia is characterized by a deficiency in blood clotting factor VIII while type B is caused by missing or defective factor IX.
Heterozygous female are those who are having mutant allele on one X chromosome and normal allele on another X. More males than females are affected. A All daughters of affected fathers are carriers.
Because of that it doesnt protect the. Characteristics of Sex X linked Recessive Trait. Biology questions and answers.
Boys and girls are equally affected. Females may experience less severe symptoms of the disorder than males. Characteristics of X-linked recessive disorders include which of the following.
Enlarged lymph nodes liver and spleen. A changed gene cannot be corrected it is present for life. A female who is a carrier has a 1 in 2 50 percent chance to pass on her X chromosome with the gene mutation for hemophilia A or B to a boy who will be affected.
However the Y chromosome doesnt contain most of the genes of the X chromosome. It is also known as daltonism. Match the following genetic abnormalities with their mode of inheritance.
The most common X-linked recessive disorders are. C The son of a carrier mother has a 25 chance of being affected. Males have only one X chromosome.
Mononucleosis may cause fatigue. And symptoms of anemia. A male will never pass on a changed gene to his son.
1 5 Dysgammaglobulinemia causes an increased risk of recurrent infections. Young adults may be prone to renal failure and myocardial infarctions. Pedigree Chart X linked Recessive Disorders.
A major characteristic of X-linked inheritance is that fathers cannot pass X-linked traits to their sons. Answers may be used more than once. Because human males need to inherit only one recessive mutant X allele to be affected X-linked disorders are disproportionately observed in males.
Examples of X-linked recessive conditions include red-green color blindness and hemophilia A. The son of a carrier females having a 25 chance of being affected. A single recessive gene on that X chromosome will cause the disease.
Is never passed from father to son. Between seven and ten percent of men and 049 to 1 of women are affected. Type A and B hemophilia are recessive genetic diseases linked to the X chromosome.
An X-linked recessive disorder with mild expression occasionally seen in carrier females this entity is caused by deficiency of the enzyme α-galactosidase α-Gal and is found in 1 of 40000 people. A male who has an X linked recessive condition will always pass on the changed gene to his daughter who will then be a carrier. A characteristic of X-linked inheritance is that fathers cannot pass X-linked traits to their sons no male-to-male transmission.
Boys and girls are equally affected. O a Recessive X-linked disorders are more common in males than in females O b. All daughters of affected fathers are carriers.
In males who have only one X. Characteristics of X-linked recessive disorders include which of the following. Characteristics of X-linked recessive disorders include which of the following.
D Affected fathers transmit the. Its commonness may be explained by its relatively benign nature. The son of a carrier mother has a 25 chance of being affected.
X-Linked traits are not found in males because males do not have any X chromosomes. Their visual acuity ability to. Because human males need to inherit only one recessive mutant X allele to be affected X-linked disorders are disproportionately observed in males.
The genes for X-inked traits are found on the Y. Multifactorial ___ Turner syndrome ___ Klinefelter syndrome ___ Huntington chorea ___ Marfan disease ___ Hemophilia A and B ___ Phenylketonuria. Which of the following statements is TRUE of X-linked traits such as color blindness in humans.
Redgreen color blindness a very common trait in humans and frequently used to explain X-linked disorders. Red-green color blindness simply means that a person cannot distinguish shades of red and green usually blue-green. They cause blood clotting problems and they are more common in males.
The son of a carrier mother has a 25 chance of being affected D. All daughters of affected fathers are carriers B. A carrier heterozygous mother produces approximately 12 affected sons.
An inflamed and sore throat. Affected fathers transmit the. Heterozygous female are those who are having mutant allele on one X chromosome and normal allele on another X.
Affected fathers transmit the gene to all of their sons C. However if he has an X linked dominant condition his daughter will be affected. Affected fathers transmitting the gene to all their sons.
Boys and girls being equally affected. B Boys and girls are equally affected. All of the above are true Od.
Affected sons are usually born to unaffected mother. Heterozygous female may have a variable expression of X linked recessive disorder due to the random process of X inactivation involving inactivation of the X chromosome with a mutant allele in some cells while. X-linked recessive diseases most often occur in males.
X-linked recessive disorders are also caused by variants in genes on the X chromosome. Sex-linkage studies in Morgans laboratory provided the fundamentals for understanding X-linked recessive disorders in humans which include red-green color blindness and Types A and B hemophilia. 3 XLP1 is caused by mutations in the SH2D1A gene and XLP2 is caused by mutations in the XIAP gene.
Thus the trait skip generations.
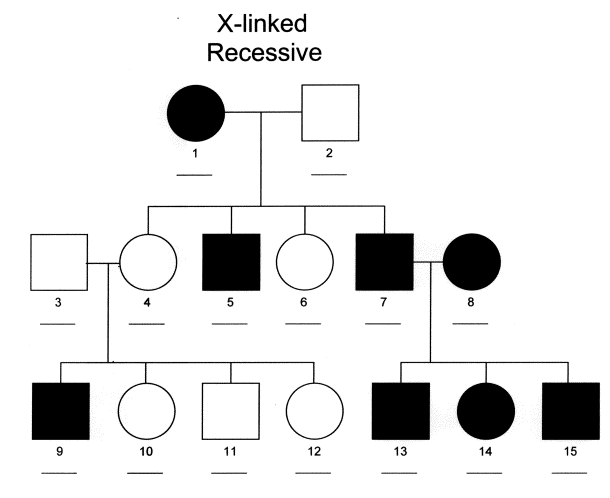
Sex X Linked Recessive Inheritance Michigan Genetics Resource Center

Definition Of X Linked Recessive Inheritance Nci Dictionary Of Genetics Terms National Cancer Institute


Comments
Post a Comment